Logos President Helio Fred Garcia was quoted extensively by major media in the March/April 2018 timeframe about Facebook’s ineffective crisis response regarding Cambridge Analytica’s misuse of Facebook users’ data.
The crisis broke Friday evening, March 16, and Facebook’s initial response was muted and legalistic. Between Friday night and Tuesday morning Facebook stock was down 9 percent, losing more than $50 billion in market value.
 Garcia was quoted first by Bloomberg View’s Kara Alaimo. In her piece, titled “Facebook’s PR Crisis Is a Mess of Its Own Making – Transparency is the best policy for one simple reason: The truth always comes out,” Alaimo says,
Garcia was quoted first by Bloomberg View’s Kara Alaimo. In her piece, titled “Facebook’s PR Crisis Is a Mess of Its Own Making – Transparency is the best policy for one simple reason: The truth always comes out,” Alaimo says,
One reason Facebook may have decided to withhold the information for so long is that it was trying to figure out how to prevent such episodes from happening again. However, companies don’t need to resolve a problem fully before they disclose it.
Helio Fred Garcia, president of the Logos Consulting Group and author of “The Agony of Decision: Mental Readiness and Leadership in a Crisis,” says that a company determining how to address a crisis should ask itself this question: “What would reasonable people appropriately expect a responsible organization or leader to do when facing this kind of situation?”
She added,
Reasonable people wouldn’t expect a company that just learned that its data has been improperly shared to have developed a full plan within minutes to prevent such a situation from recurring. They would, however, expect the company to be transparent, express remorse, pledge to take action to prevent the problem from happening again, and follow up with an announcement about what it was doing to solve the underlying issue. If Facebook had done this, it wouldn’t be dealing with the mess it’s in today.

Garcia was also interviewed by the Associated Press. In its story titled “Crisis Management: What Not to Do,” appeared initially in The Washington Post.

The AP story says,
The point is to at least make an effort to seem remorseful to win back public trust, experts say. But despite user outcry on its own Facebook page and a call from Congress for Zuckerberg to testify about Facebook’s role in election-meddling, Facebook seems to be charting its own course.
It’s a pattern Facebook has long followed, said Helio Fred Garcia, a professor of crisis management at NYU and Columbia University in New York. Facebook hedged during its early days in 2007 over a controversial advertising program called Beacon that did not alert users it was sharing their activity, and it did so again in its response to Russian bots hijacking Facebook ad software during the Trump campaign in 2016.
“Facebook has been too late. Facebook has done too little and has been too legalistic’ each time, Garcia said. ‘I have yet to find a crisis Facebook handled that I could stand in front of crisis management classes and say, ‘Here’s an example of how to handle a crisis.’ They’ve never been able to handle a crisis.”
Once Zuckerberg addresses the public, the PR flap may eventually be forgotten. But it will take a lot longer than if the company had addressed public concerns immediately, Garcia said.
“It’s much harder to restore trust once it has been lost than to preserve trust before it has been lost,” he said.
About an hour after the original AP story appeared, Mark Zuckerberg, CEO of Facebook, released his first written public comment. The AP interviewed Garcia for his reaction, and then updated its story to include Mr. Zuckerberg’s statement and Garcia’s comments on it.
“My biggest skepticism is that we’ve seen this play before,” said Helio Fred Garcia, a professor of crisis management at NYU and Columbia University in New York. “They’re caught coming short of customers’ privacy expectations. They tweak procedures. But they don’t seem to learn from mistakes, don’t really seem to care.”

That night Mr. Zuckerberg made his firs personal public statement, on an exclusive interview on CNN. You can see the entire interview here. The Associated Press asked Garcia to comment on the interview. It reported:
“On Wednesday, the generally reclusive Zuckerberg sat for an interview on CNN and conducted several more with other outlets, addressing reports that Cambridge Analytica purloined the data of more than 50 million Facebook users in order to sway elections. The Trump campaign paid the firm $6 million during the 2016 election, although it has since distanced itself from Cambridge.
Zuckerberg apologized for a ‘major breach of trust,’ admitted mistakes and outlined steps to protect users following Cambridge’s data grab. His mea culpa on cable television came a few hours after he acknowledged his company’s mistakes in a Facebook post, but without saying he was sorry.

‘I am really sorry that happened,’ Zuckerberg said on CNN. Facebook has a ‘responsibility’ to protect its users’ data, he added, noting that if it fails, ‘we don’t deserve to have the opportunity to serve people.’
While several experts said Zuckerberg took an important step with the CNN interview, few were convinced that he put the Cambridge issue behind hm. Zuckerberg’s apology, for instance, seemed rushed and pro forma to Helio Fred Garcia, a crisis-management professor at NYU and Columbia University.
‘He didn’t acknowledge the harm or potential harm to the affected users,” Garcia said. “I doubt most people realized he was apologizing.’

The next morning Canadian Broadcasting Corporation News interviewed Garcia and asked him to grade Mr. Zuckerberg’s apology.
Garcia said,
‘The most charitable grade I can give Mr. Zuckerberg for last night’s interview would be a B-minus. But it’s in a context where an A was necessary to get out of the mess that he is in. That interview called for leadership and confidence and commitment. And we got something just short of that.’
Regarding the apology itself, I’m really sorry that this happened, “Garcia said,
‘When I heard that I said, Gosh, I hope that’s the only time we hear Sorry in this interview. Because he didn’t say what he was sorry for, he didn’t say whom he was sorry to, he did not say it in a manner that suggested regret or remorse. He suggested it in a way that he seemed to be getting through it and checking off a box. Even the word ‘sorry,’ he swallowed the word when he pronounced it. Someone would have been forgiven for not noticing the apology. And he didn’t repeat it later in the interview.’
Asked about testifying before Congress, Mr. Zuckerberg said that he’d testify to Congress if it was the right thing to do, but that his inclination was to send the person at Facebook who had the most detailed knowledge on the topic that Congress wants to speak about. And that if that were him, he’d be happy to testify. Asked what he heard in that statement, Garcia said,
‘I heard an opportunity where a leader is needed and instead we heard from a technocrat. The burden of leadership is to represent the company to those who matter the most… The leader’s duty is to represent the company. He is speaking as if it’s about an exchange of knowledge, but Congressional testimony is about leadership accountability, and that’s what was missing here.’
Asked about Facebook’s response to the crisis, Garcia said,
‘One of my criticisms of Facebook in general is that we’ve seen this play before. We saw it eleven years ago with their first first big crisis involving a product called Beacon, where the pattern was silence, then, oh, it’s not that bad, and then an apology and then a tweaking of procedure. We saw it again after the Federal Trade Commission fined Facebook for privacy violations. The same pattern: Silence and then acknowledgement and then a kind of apology and then a tweak in procedures. We saw it after the Russian advertising in the American political process scandal last year.
This pattern happens again and again. I give them credit for saying ‘We got it wrong.’ I give them credit for saying ‘We’ve got to get it right.’ That’s why it gets to a B-minus. But the idea that 50 million customers had their information compromised and that Facebook knew about it three years ago, and only now commits to notify those who were affected that they may have been affected, that is a failure. It is a failure of leadership and a failure of responsibility.’
You can watch the entire interview here.
The following week, on March 27, Garcia was interviewed live by Canada’s CTV News on what Zuckerberg apparent hesitation to commit to testify before a Senate committee on April 10, two weeks later, but rather offering to send Facebook technical experts instead. Garcia said,
‘This is a moment that calls for leadership. But Mr. Zuckerberg is behaving like a technocrat. It is the duty of the CEO to represent the company to all who matter. And a parliamentary hearing, a congressional hearing, calls for a leader to be there, for the boss to be there. Congressional hearings are not about a transfer of knowledge. Congressional hearings are about accountability and and responsibility. Now if Mr. Zuckerberg were to show up with his technical experts, that would be fine. But he seems to be evading an important responsibility of being the CEO.’
Asked what the hesitation could be about and whether Mr. Zuckerberg would be getting counsel from lawyers, Garcia said,
‘I would assume that that’s the case. One of the things we know is that congressional hearings aren’t merely about public policy. They are also about politicians using the bully pulpit of a congressional hearing to show themselves to be tough, and to be tough on companies that are seen to be behaving inappropriately. And can see the human impulse to want to avoid that kind of embarrassment, but that’s the one of the burdens of leadership, to face into the difficult situations. The idea that he would not appear in front of a congressional committee when his stock has lost already more than $100 billion in value, when customers are worrying about whether Facebook has misappropriated their data, these are all very concerning things and he is not behaving the way a CEO is supposed to behave.’
He was asked whether this is the beginning of the end, and whether the world could continue without Facebook, Garcia replied,
‘The company has made the wrong choice at every turning point since the crisis began. And the crisis began three years ago when they discovered that 50 million customers had their information misappropriated and chose not to notify those customers. They didn’t commit to notifying those customers until a week ago. The company is facing a critical turning point. There was a time when I couldn’t live without Blockbuster Video. That time has passed. There was a time when I couldn’t live without Borders bookstore. That time has passed. And it is completely within the control of the leaders at Facebook whether Facebook remains relevant and trusted. But for that they are going to have to step up in this turning point because if they fail to step up someone will build a better mousetrap and people will move to a different platform.
You can see the entire interview here.
 On Sunday, April 1, the Associated Press quoted Garcia on the preparation Mr. Zuckerberg would likely need to do before his scheduled April 11 testimony. As it appeared in Mr. Zuckerberg’s hometown newspaper, The San Francisco Chronicle, the story quoted and paraphrased Garcia as follows:
On Sunday, April 1, the Associated Press quoted Garcia on the preparation Mr. Zuckerberg would likely need to do before his scheduled April 11 testimony. As it appeared in Mr. Zuckerberg’s hometown newspaper, The San Francisco Chronicle, the story quoted and paraphrased Garcia as follows:
“Helio Fred Garcia, who as president of Logos Consulting Group has prepped unnamed banking, pharmaceutical and other executives, said a CEO client of his went through a mock hearing in which someone said very harsh things to rattle him. He was shown video of his expression to make sure he wouldn’t replicate it in front of the Senate. The verdict? ‘He kept his job, so it went fine,’ Garcia said.”
It added,
“CEOs may be used to getting their own way, but they aren’t in control during hearings. Garcia said that can cause them ‘a great deal of distress.’
Zuckerberg has to understand he’s a target and swallow his pride. His job isn’t to try to persuade the senators of anything, but to let senators express their anger.
‘This isn’t an educational forum,’ Garcia said. ‘It’s a highly ritualized piece of theater.’
It continued,
“At the same time, Zuckerberg can’t get too bogged down in technical explanations, Garcia said. A hearing puts the spotlight on leadership and accountability, not technical details. Garcia said Zuckerberg has to ‘speak in leadership terms: ‘This was a massive failure and I apologize.””
 April 11, the day of the Senate hearing, Garcia was again quoted by Associated Press. As appeared in the New York Times and Washington Post, Garcia was quoted assessing Mr. Zuckerberg’s testimony as follows:
April 11, the day of the Senate hearing, Garcia was again quoted by Associated Press. As appeared in the New York Times and Washington Post, Garcia was quoted assessing Mr. Zuckerberg’s testimony as follows:
[The senators] allowed Zuckerberg to repeat his talking points — that Facebook doesn’t own or sell users data, that he and other senior executives weren’t proactive enough with Cambridge Analytica but they’ve changed that, and that using artificial intelligence in elections to stop fake accounts is a top priority.
The result?
“He’s giving the same responses to the same questions from different senators,” said Helio Fred Garcia, a professor of crisis management at NYU and Columbia University in New York.
Zuckerberg seemed often to retreat to three “safe havens,” Garcia said:
One, diffusing responsibility to his “team.”
Two, when pressed on policy issues, agreeing to a principle without committing to details.
And three, never failing in answering questions to start by addressing the questioner as “senator” or “congressman.”
“He’s diligent in showing deference and respect,” Garcia said.
In addition to his client work through Logos Consulting Group Garcia is an adjunct professor of management at NYU’s Stern School of Business Executive MBA program, where he teaches crisis management. He also teaches crisis communication in NYU’s School of Professional Studies MS in Public Relations and Corporate Communication. He is also an adjunct associate professor in Columbia University’s Fu Foundation School of Engineering, where he teaches crisis management, ethics, and leadership in the Professional Development and Leadership Program.
Garcia is the author most recently of The Agony of Decision: Mental Readiness and Leadership in a Crisis, available in both paperback and as an e-book from Kindle here.






 Garcia was quoted first by Bloomberg View’s
Garcia was quoted first by Bloomberg View’s 





 On Sunday, April 1, the Associated Press quoted Garcia on the preparation Mr. Zuckerberg would likely need to do before his scheduled April 11 testimony. As it appeared in Mr. Zuckerberg’s hometown newspaper,
On Sunday, April 1, the Associated Press quoted Garcia on the preparation Mr. Zuckerberg would likely need to do before his scheduled April 11 testimony. As it appeared in Mr. Zuckerberg’s hometown newspaper, 




















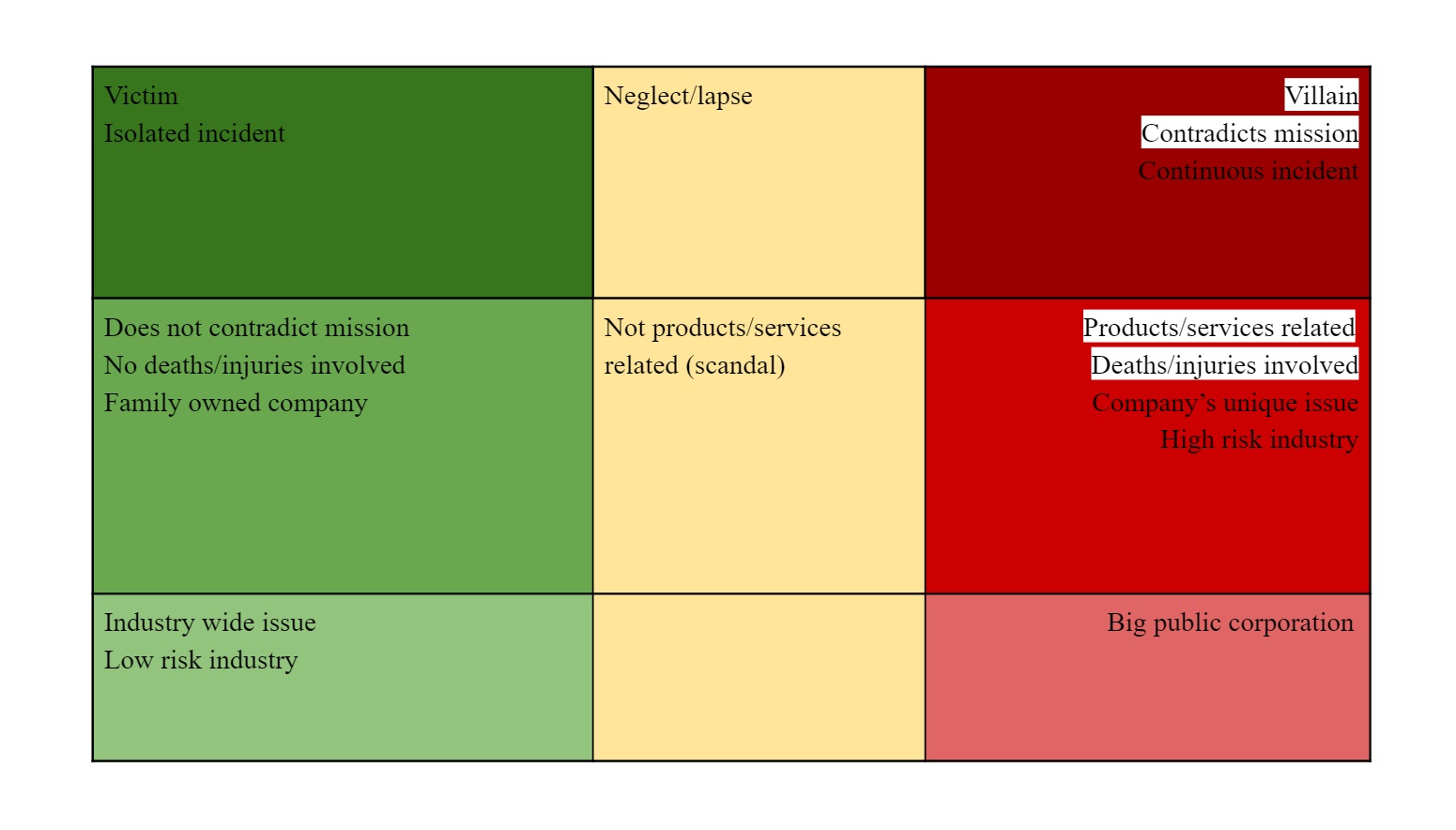
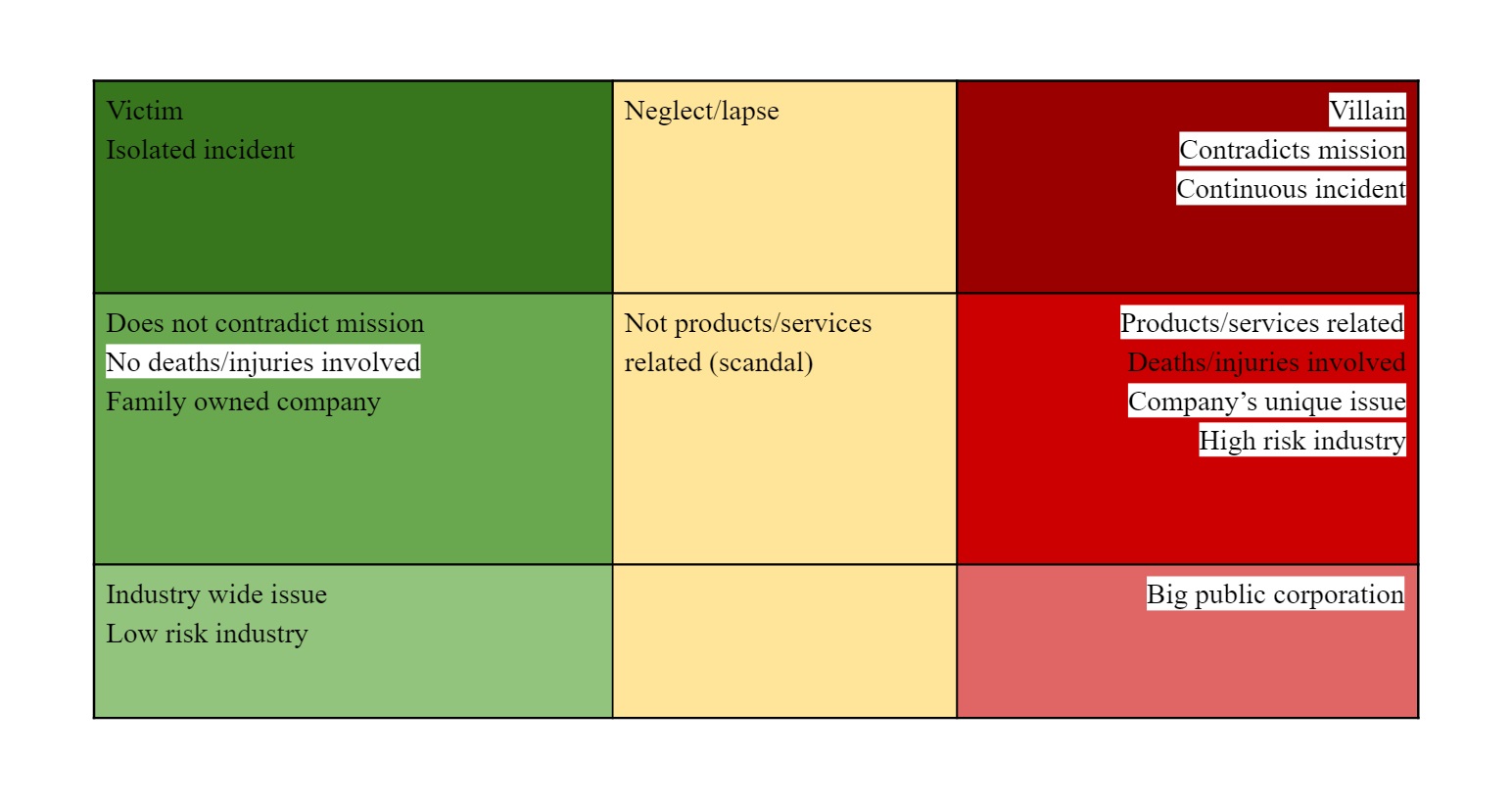
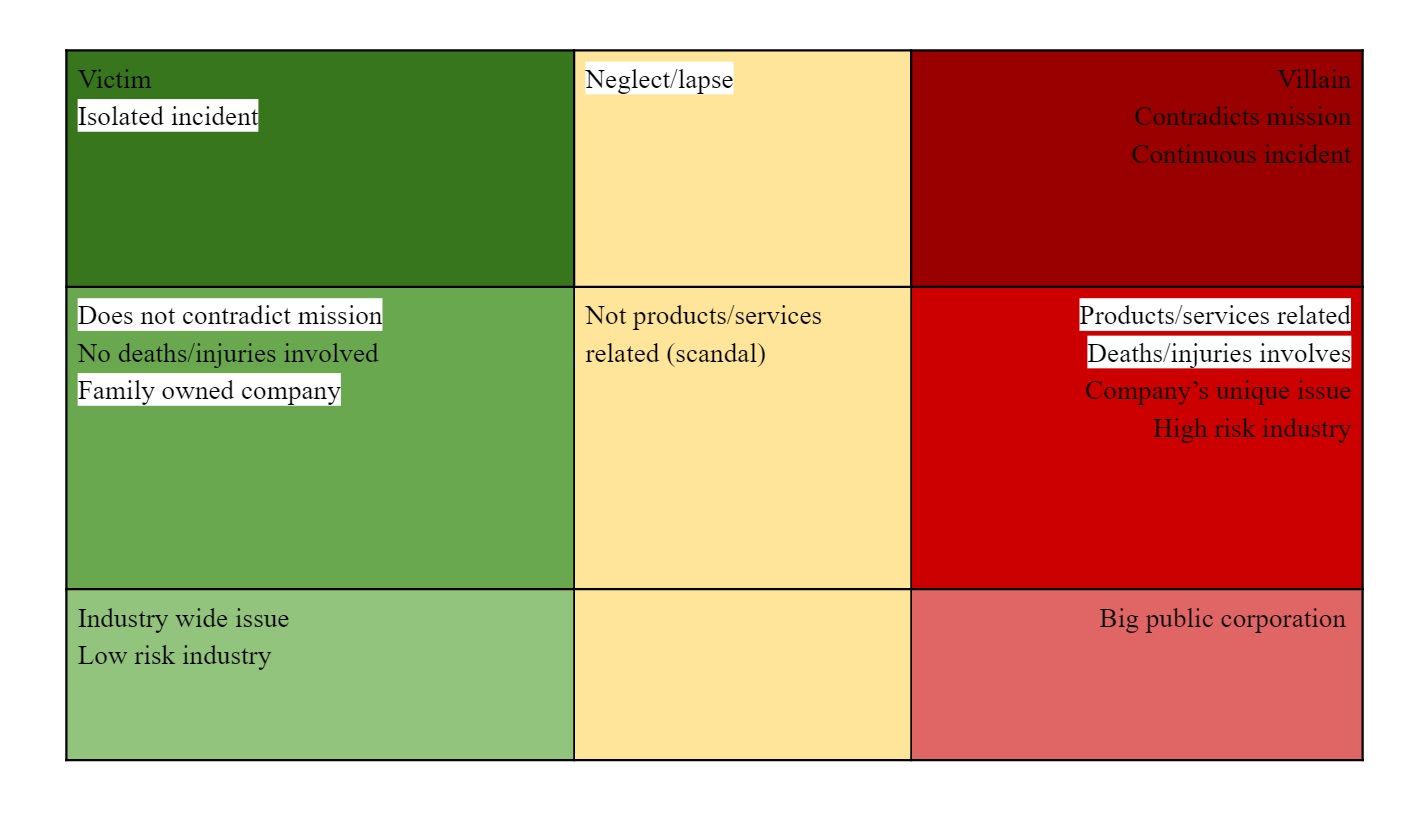
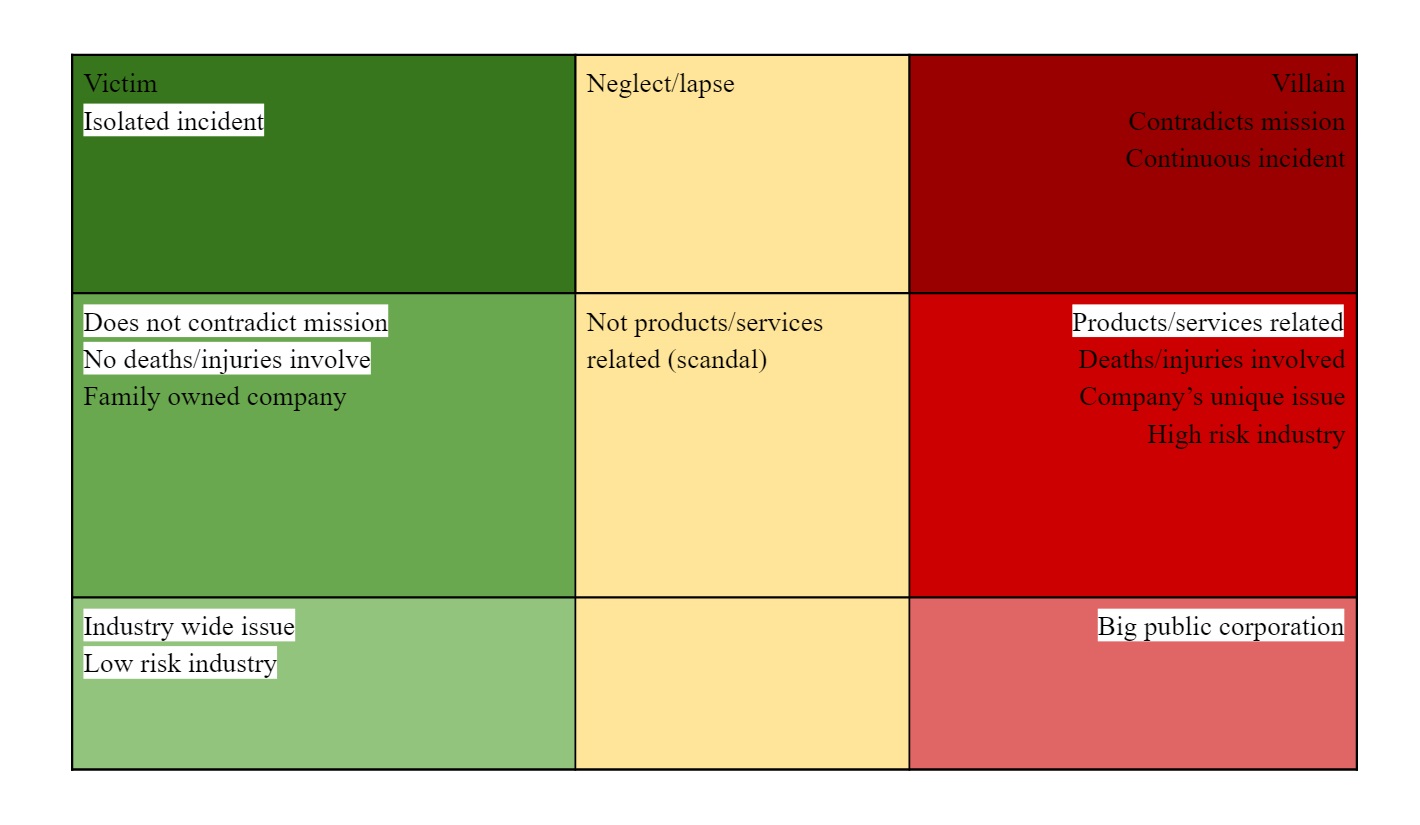
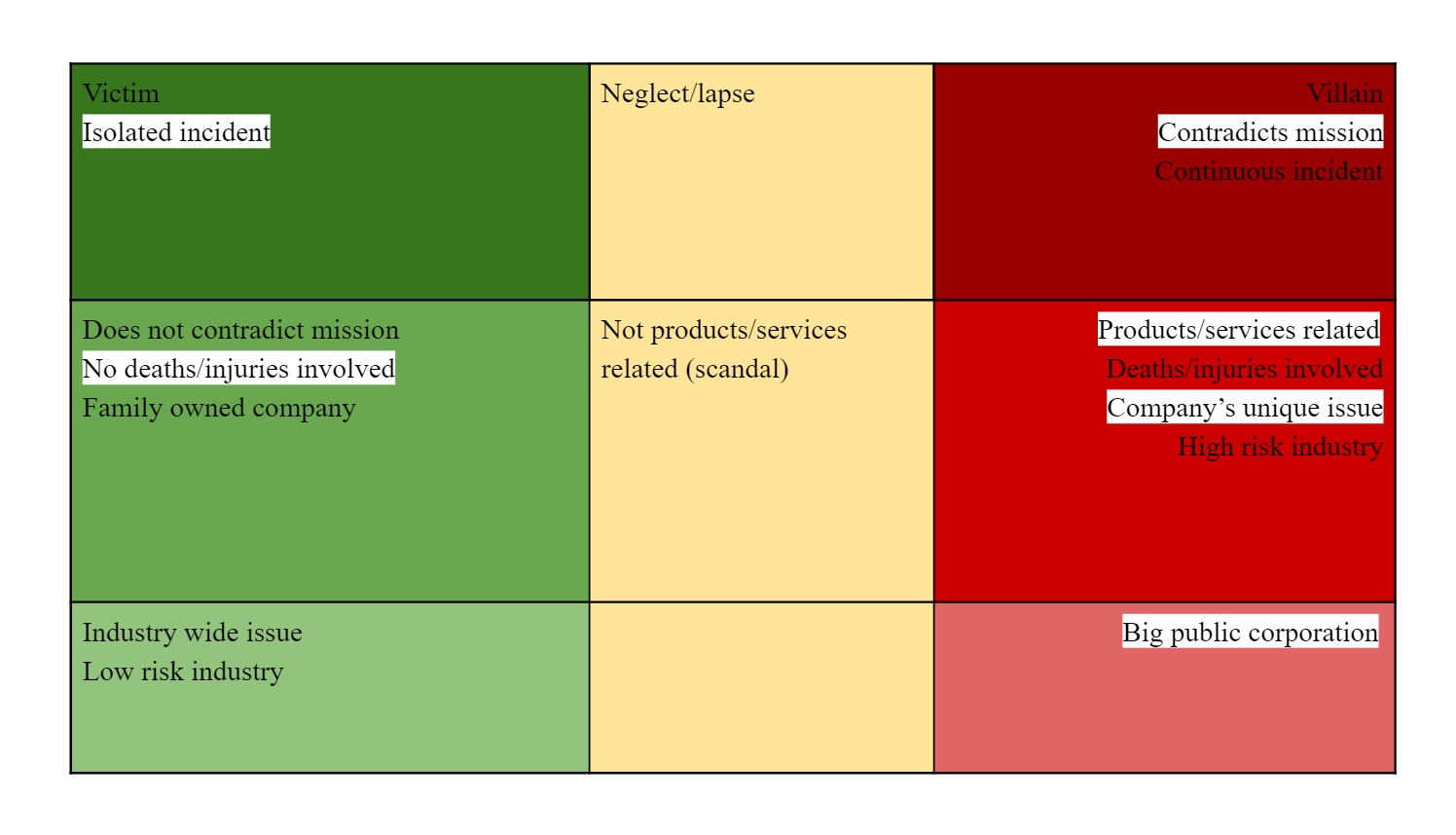
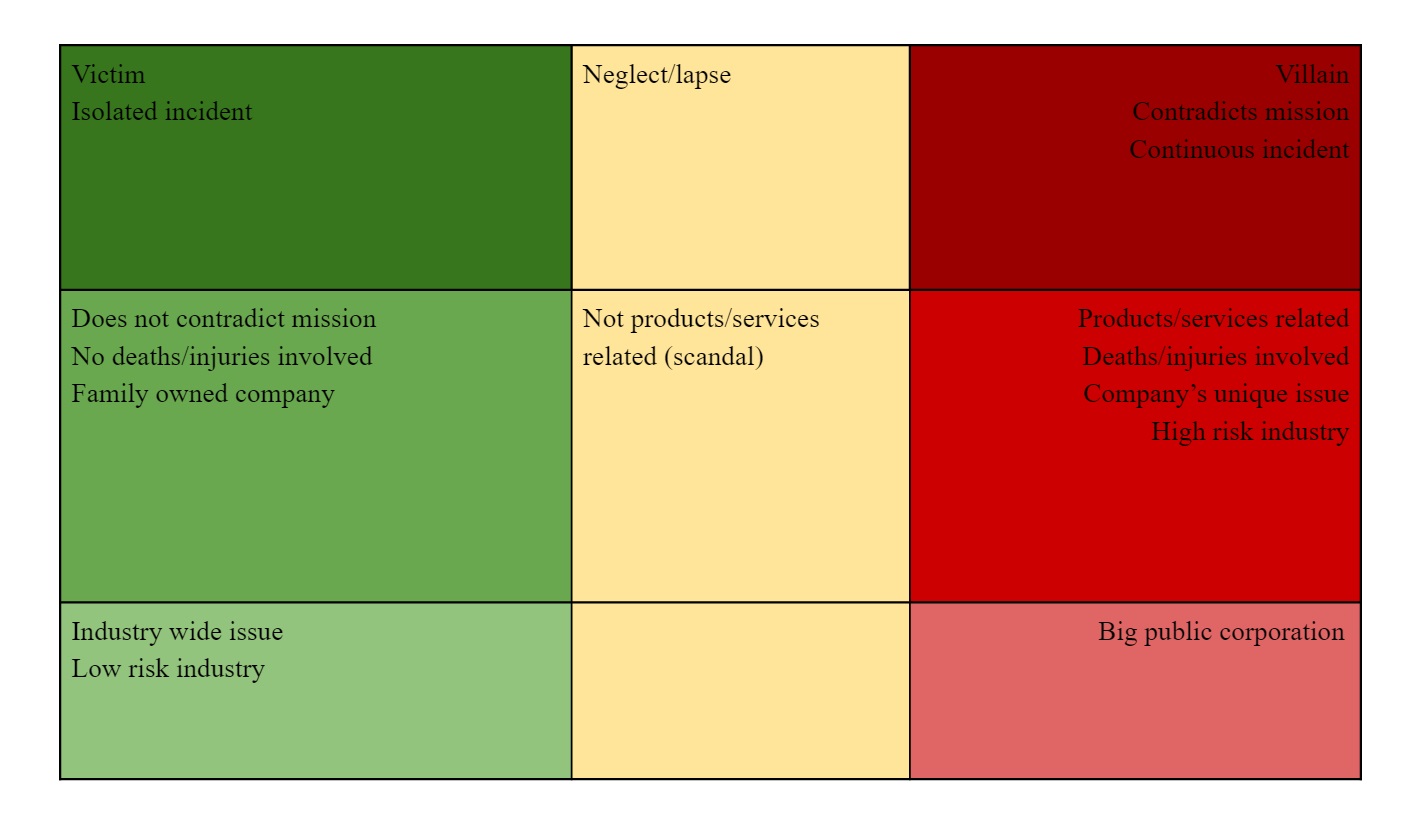 Brand loyalty is more likely to help a brand under conditions in the left column (green), and more likely to harm one under conditions in the right column (red).
Brand loyalty is more likely to help a brand under conditions in the left column (green), and more likely to harm one under conditions in the right column (red).


 On January 31, 2012, the Susan G Komen Foundation announced its decision to stop funding Planned Parenthood.
On January 31, 2012, the Susan G Komen Foundation announced its decision to stop funding Planned Parenthood.